Climate Change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in global or regional climate patterns, including changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events, attributed largely to human activities. While global warming specifically refers to the increase in Earth's average surface temperature, climate change encompasses a broader range of environmental impacts resulting from this warming.
Key aspects of climate change include:
- 1. "Temperature rise:" The average global temperature has been increasing steadily, leading to warmer temperatures overall. This warming trend is linked to the buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, primarily from burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
- 2. "Changes in precipitation patterns:" Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, leading to changes in rainfall intensity, frequency, and distribution. Some regions may experience more frequent and intense rainfall, while others may face prolonged droughts.
- 3. "Extreme weather events:" Climate change is associated with an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, typhoons, floods, droughts, heatwaves, and wildfires. These events can have devastating impacts on communities, infrastructure, agriculture, and ecosystems.
- 4. "Melting ice and rising sea levels:" Rising temperatures are causing polar ice caps, glaciers, and ice sheets to melt, contributing to rising sea levels. This poses threats to coastal communities, habitats, and infrastructure, increasing the risk of coastal flooding and erosion.
- 5. "Ocean acidification:" The absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the oceans leads to ocean acidification, which can have detrimental effects on marine life, particularly coral reefs and shell-forming organisms.
Addressing climate change requires urgent and concerted efforts at the global, national, and local levels. Strategies include reducing greenhouse gas emissions by transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, implementing policies to promote sustainable land use and transportation, enhancing resilience to climate impacts, and fostering international cooperation. Individuals can also contribute by adopting sustainable practices in their daily lives, advocating for climate action, and supporting initiatives that mitigate climate change and its impacts.

- Details
- Category: Climate Change
- 169
For years, solar geoengineering has floated around the internet as a supposed secret plan to “control the weather” or dim the Sun itself. The reality is far less dramatic — and far more cautious. What scientists are actually studying is a controversial, last-resort idea to slightly reflect sunlight in order to temporarily slow warming, not a hidden climate switch. Even then, most researchers stress it would carry serious risks and cannot replace cutting emissions.
- Details
- Category: Climate Change
- 167
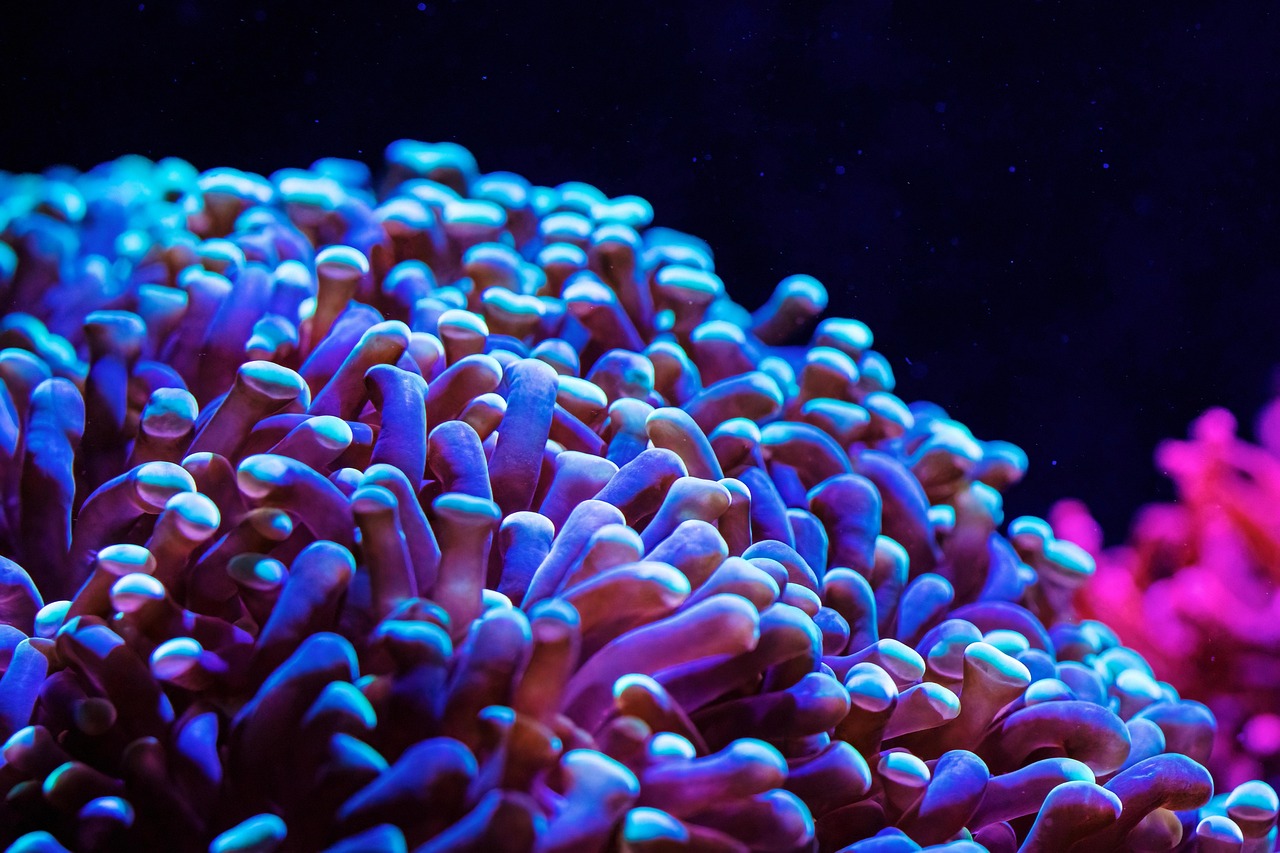
Short answer: no — not “point of no return” globally, but some reefs are already lost, and many more are in serious danger.
- Details
- Category: Climate Change
- 1099
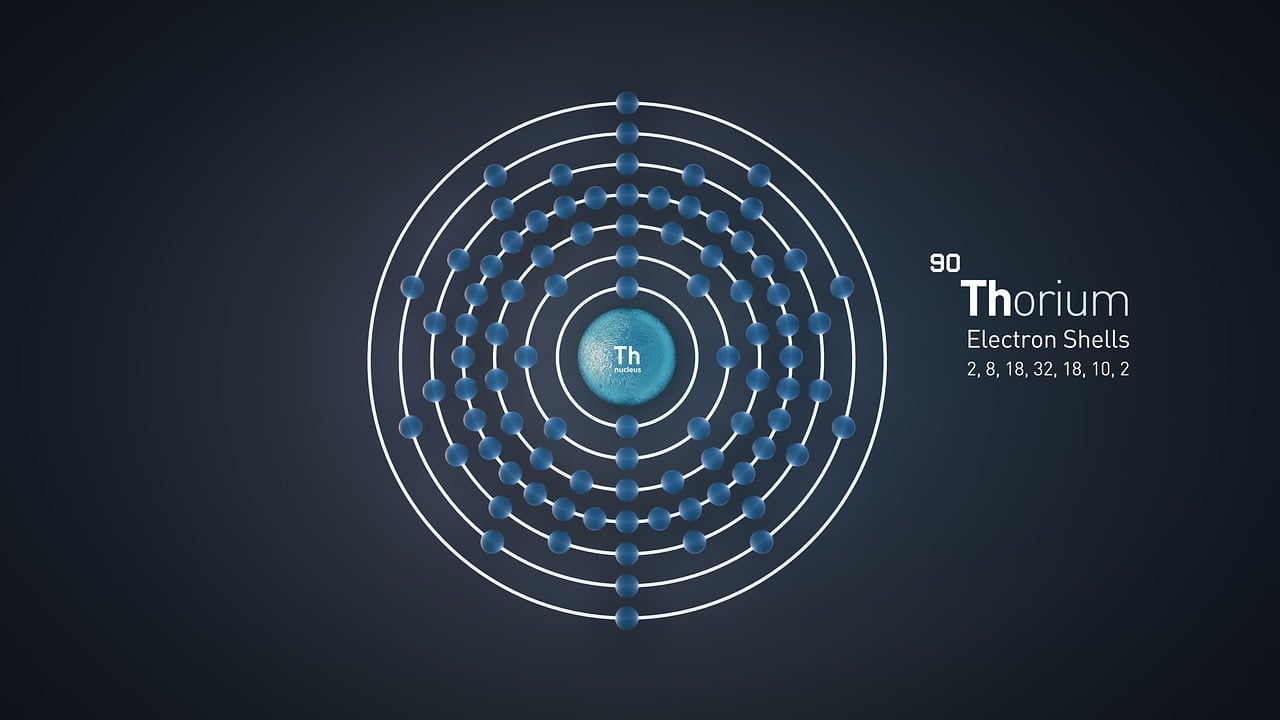
Thorium (Th) is a naturally occurring radioactive element (atomic number 90) that has gained attention as a potential fuel for nuclear reactors. It is about three to four times more abundant in the Earth's crust than uranium and is primarily found in monazite sands.
Why Thorium for Nuclear Power?
Thorium itself is not fissile, meaning it cannot directly sustain a nuclear chain reaction. However, when bombarded with neutrons, thorium-232 can absorb a neutron and eventually transmute into uranium-233 (U-233), which is fissile and can be used as nuclear fuel.